Photo: © Video screenshot

Photo: © Video screenshot
What doesn’t fly in orbit: old probes, spent rocket stages, fragments of skin. Around the Earth now rotates about 130 million objects that are recognized as space debris. And very soon it will all begin to pour on people’s heads. According to scientists, by 2030 the probability of death from space debris will increase by 10%. About how to clean up outer space from debris, tells program “Science and Technology” with host Mikhail Borzenkov on REN TV.
Clutter in low Earth orbit
On September 7, 2020, residents of the Chinese village of Lilong noticed an unidentified object in the sky. It was descending at great speed, and when it hit the ground, it exploded and caught fire. On that day, an Earth sensing satellite was launched from the Taiyuan Cosmodrome. The engineers miscalculated the trajectory of the fall. One of the separated stages of the rocket hit the village.
And this is not the only such case. Space junk is getting more and more dangerous. According to the European Space Agency, nine thousand tons of waste have accumulated in orbit. A special map allows you to visually assess the extent of pollution of the near-Earth space. It displays active satellites and space debris. Earth orbit is so cluttered that it is difficult to distinguish the outlines of the continents.
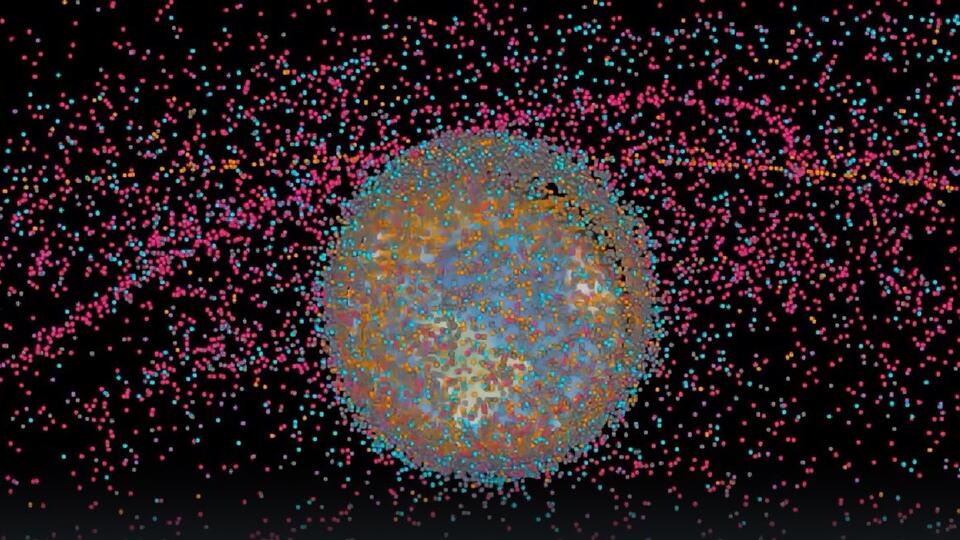
Every year there are more and more debris. If this continues, it will soon be impossible to launch new satellites: there will simply be no room for them in orbit, and the largest fragments of space debris will begin to fall to Earth. How to eliminate the threat, Japanese experts came up with.
“This is a cleaning satellite. It weighs 175 kilograms and is powered by a magnet that attracts debris to itself.”– explained the curator of the program, a senior researcher at the company – the developer of the cleaning satellite Azamu Sato.
Such debris traps will find spacecraft fragments using sensors, get closer to them, and then dock to the debris using powerful magnets. Next, the space scavenger will tow the waste into the atmosphere, where it will simply burn.
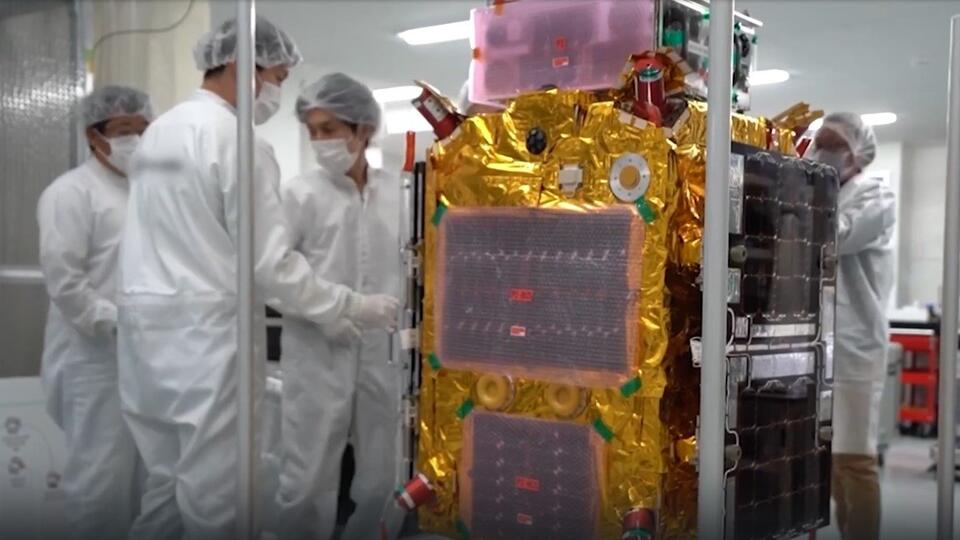

Orbital cleaner from Omsk
In 2021, the Japanese have tested their technology and proven it works. The truth turned out: in order to magnetize an object, the satellite needs to spend a lot of time and fuel. At this rate, a major space cleanup could drag on for centuries and cost billions of dollars.
The solution to the problem was proposed in Omsk. They developed a space scavenger just two by two meters in size. It is fuel efficient and easy to maneuver. The satellite quickly flies up to the wreckage and catches it on a cable, and then begins to spin along with the cargo.
“There is a centrifugal force that stretches, on the one hand, the debris, and on the other hand, the upper stage, on which the propulsion system is located. These forces are balanced, and subtlety is obtained: we make an impulse in the direction of the cable, the cable is displaced”– said Valery Trushlyakov, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor of the Aircraft and Rocket Engineering Department of the Omsk State Technical University.

Due to the centrifugal force, the satellite drags the fragment into the atmosphere. Both garbage and the spacecraft burn there. All orbital cleaners are essentially disposable. This is their main problem. Therefore, cheap Russian devices have great prospects.
swiss garbage truck
In Switzerland, they did not spare money for space cleaning and came up with a garbage truck called “Clean Space”. The European Space Agency has allocated a whopping $100 million for this project. The launch of the mission is scheduled for 2025.
“The first target will be Vespa. The mechanical device weighs 112 kilograms. It was needed to launch several satellites into orbit with one launch vehicle at once. Vespa is now not controlled by the earth authorities. It revolves around the Earth at an altitude of 800 kilometers. axes. This is one of the most complex objects in orbit.”– said the director of the Swiss space center Volker Gass.
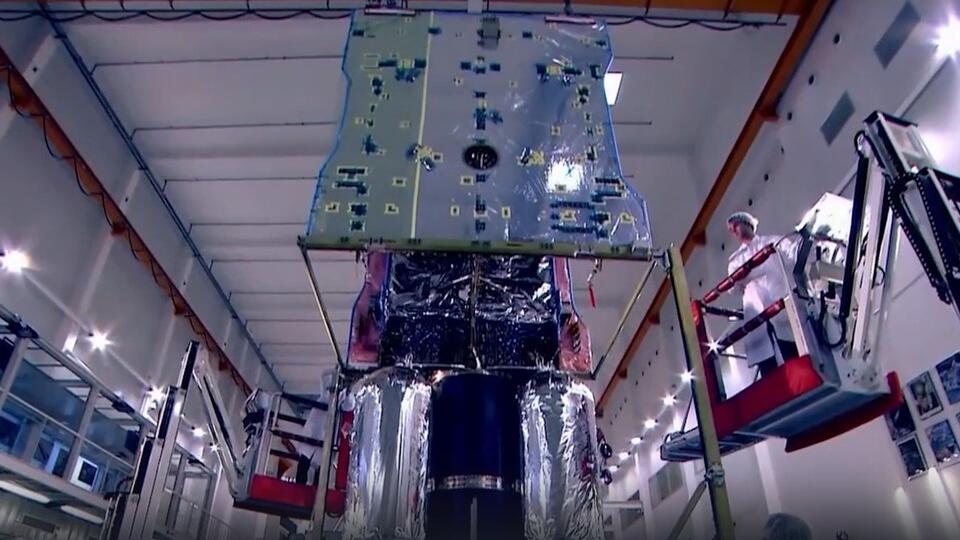

The garbage truck will use artificial intelligence to calculate the flight path, detect the satellite and grab it with manipulator arms. It seemed like a pretty simple task. But in space, it will require jewelry precision.
“In sci-fi movies, you can often see how an astronaut tries to catch a tool, but if he makes one awkward movement, the tool flies into space like a golf ball. Vespa can happen exactly the same”– said Muriel Richard, a researcher at the Swiss Space Center.
Chinese space parachute
To catch such a weighty object, the garbage truck will have to use all four manipulators. He will have to approach the Vespa at minimum speed, spread his arms wide and slowly embrace her, and then tow her to the atmosphere for disposal.
The scheme appears to be effective. But is it worth spending $100 million to destroy one of the 130 million objects in orbit? The Swiss are sure it’s worth it. Indeed, in the future they want to teach their device to capture and tow up to 10 objects at a time. True, on the scale of space cleaning, this is a drop in the ocean. But the main problem is different: garbage-carrying satellites are put into orbit with the help of rockets that discard spent stages and produce new garbage.
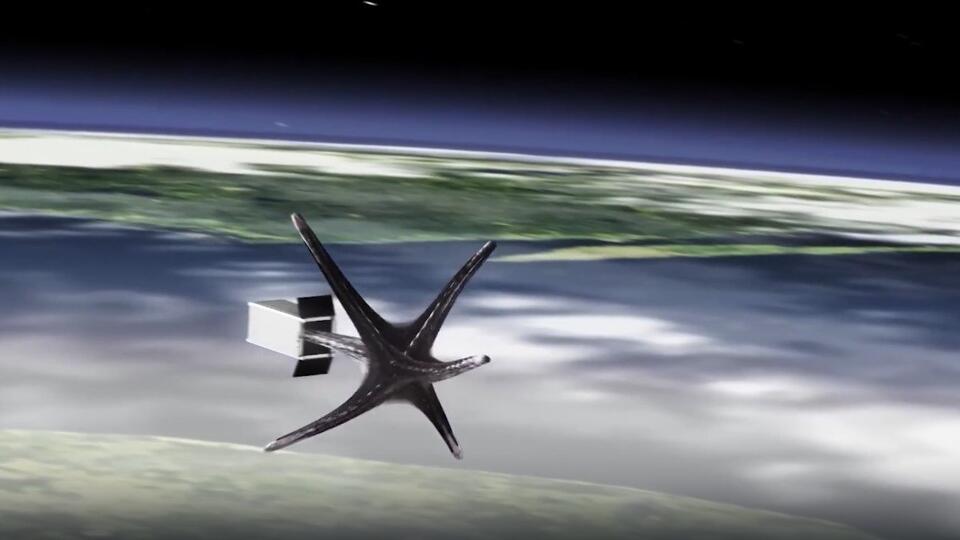

The Shanghai Academy of Space Technology is sure that in order to be clean in orbit, you need to immediately clean up after yourself. Scientists propose to attach a special brake parachute to each device even before launch. After completing the mission, it will open up and pull the unnecessary ship out of orbit into the atmosphere.
“The principle of operation is based on the fact that with a large surface area, the brake sail will accelerate the process of returning satellites and rockets due to atmospheric friction. The Earth’s gravity will do the rest”says Li Dong, senior designer at the China Rocketry Research Institute.
The Chinese are already testing their parachute in space. It was installed on a rocket that launched the world’s first quantum communications satellite into orbit.
“It is placed on the payload adapter and consists of several petals of foil on telescopic rails. The total area of the sail is about 25 square meters. The sail allows you to set the trajectory and protect other spacecraft from a collision with a spent rocket.”– said Li Dong.
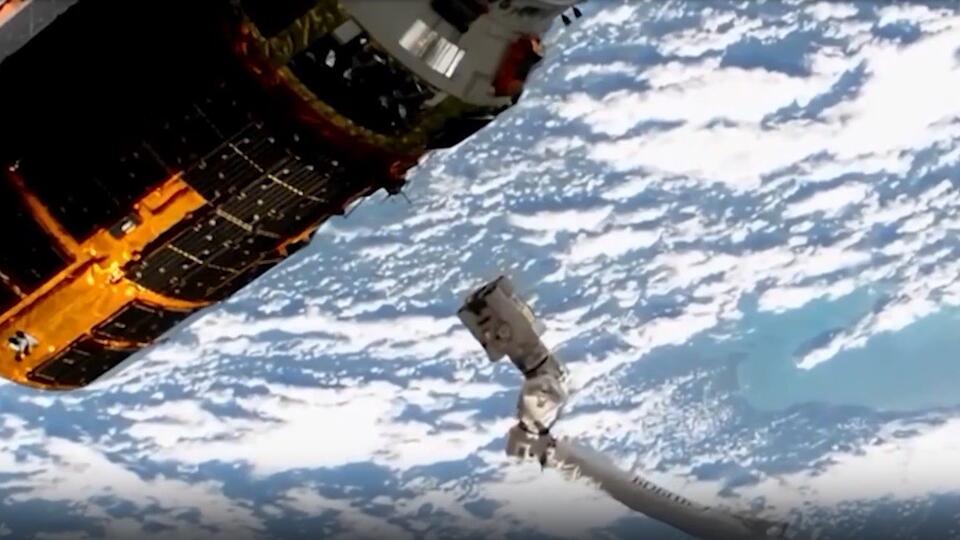

In June 2022, a rocket with a sail separated from the satellite and is now heading into the dense layers of the atmosphere. According to calculations, the ship should burn out in two years. At the same time, without a parachute, he would hang out in orbit for about 100 years.
Chinese development will help rid space of new waste, but the old ones have yet to be dealt with. Experts say that burning debris in the atmosphere is not a panacea. Now scientists around the world are looking for a way that will allow recycling garbage directly in orbit. Perhaps in the future, humanity will be able to build new spaceships from recycled materials and save a lot of money on launching vehicles from Earth.
About the most incredible achievements of progress, the discoveries of scientists, innovations that can change the future of mankind, see the program “Science and Technology” with host Mikhail Borzenkov on REN TV.
Source: Ren
Alfred Hart is an accomplished journalist known for his expert analysis and commentary on global affairs. He currently works as a writer at 24 news breaker, where he provides readers with in-depth coverage of the most pressing issues affecting the world today. With a keen insight and a deep understanding of international politics and economics, Alfred’s writing is a must-read for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the world we live in.
